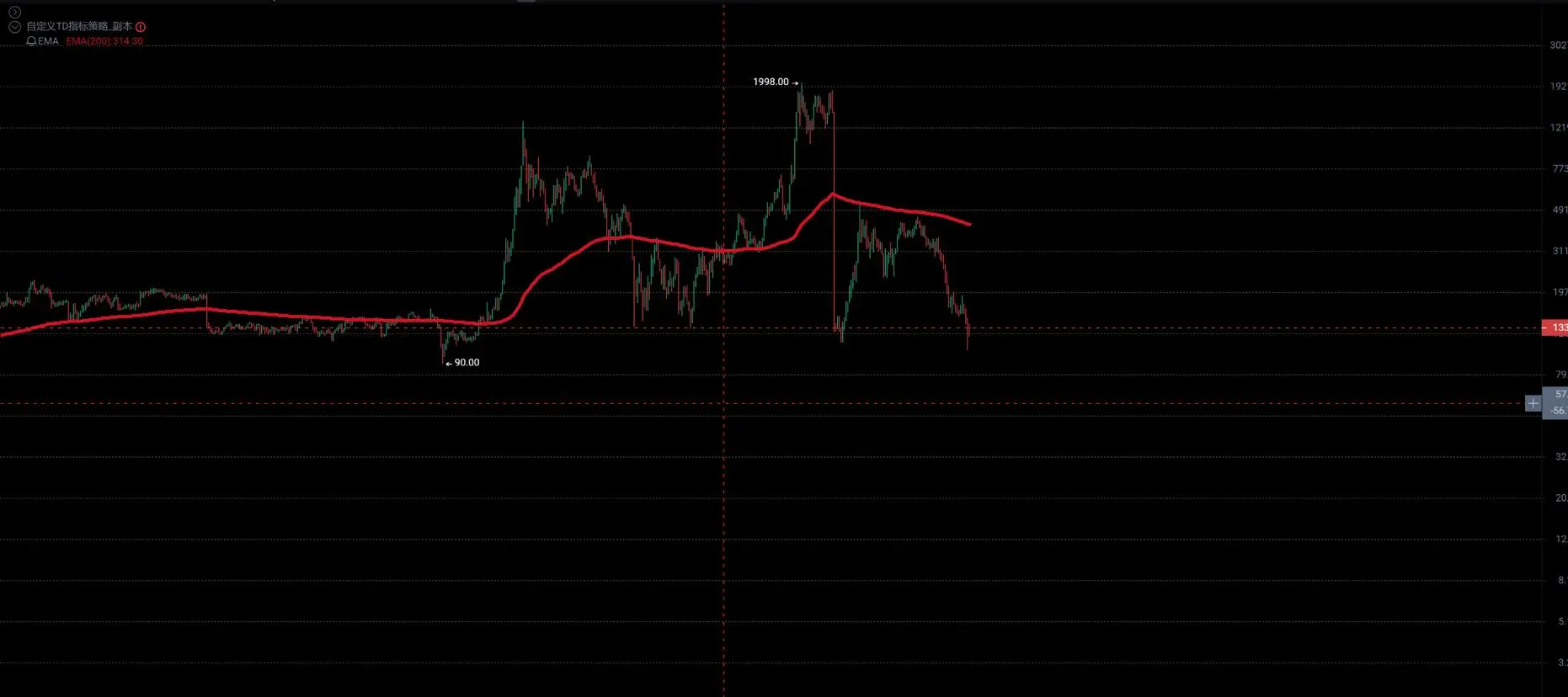
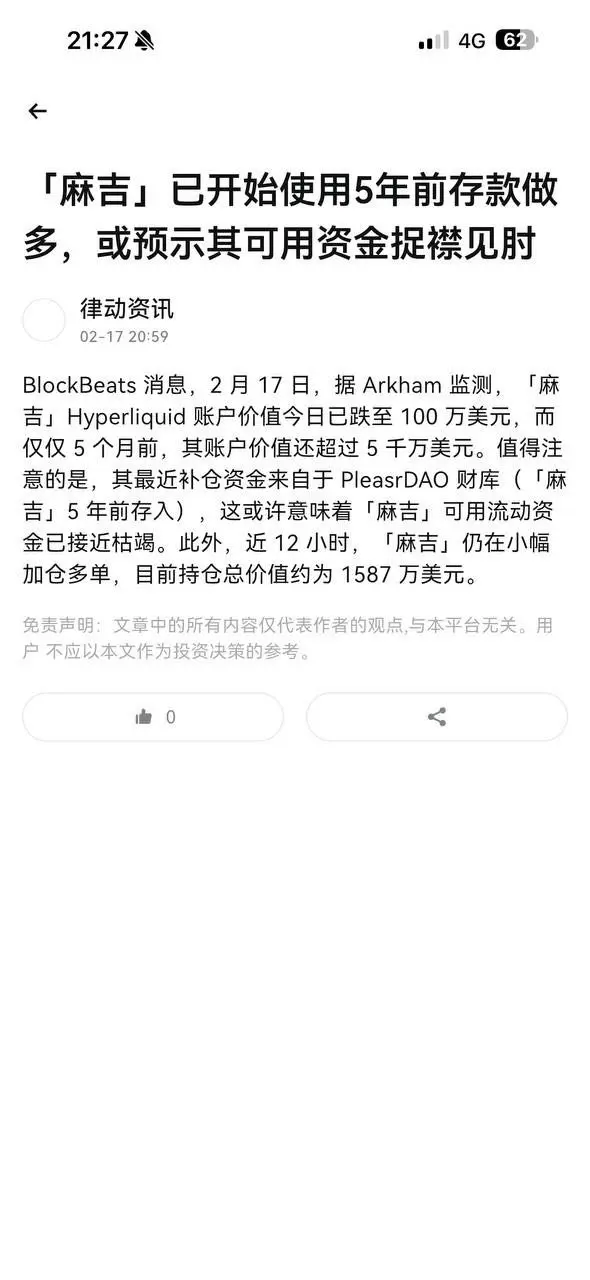
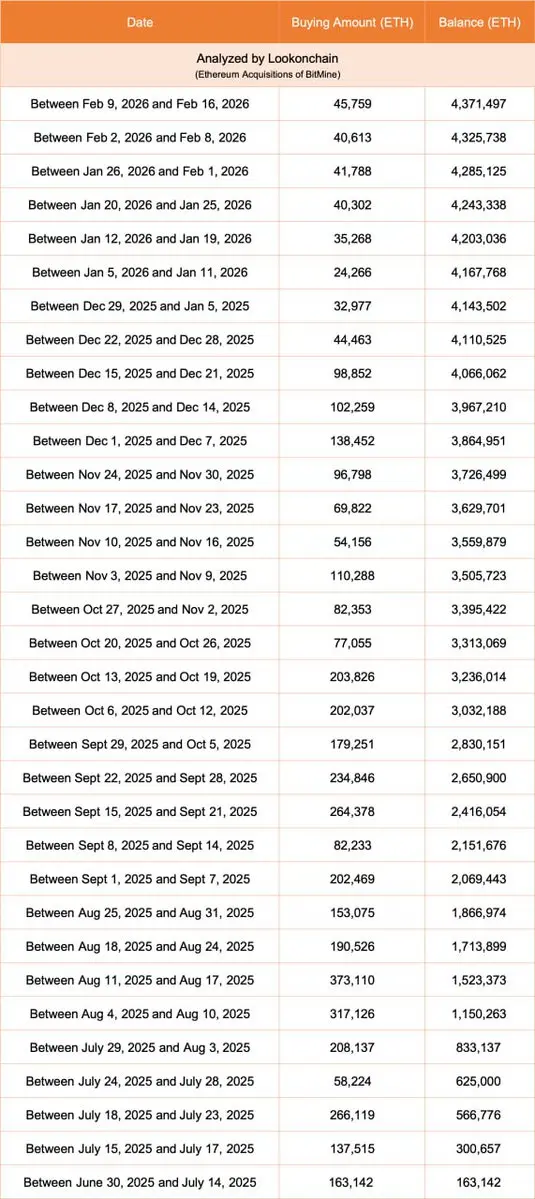
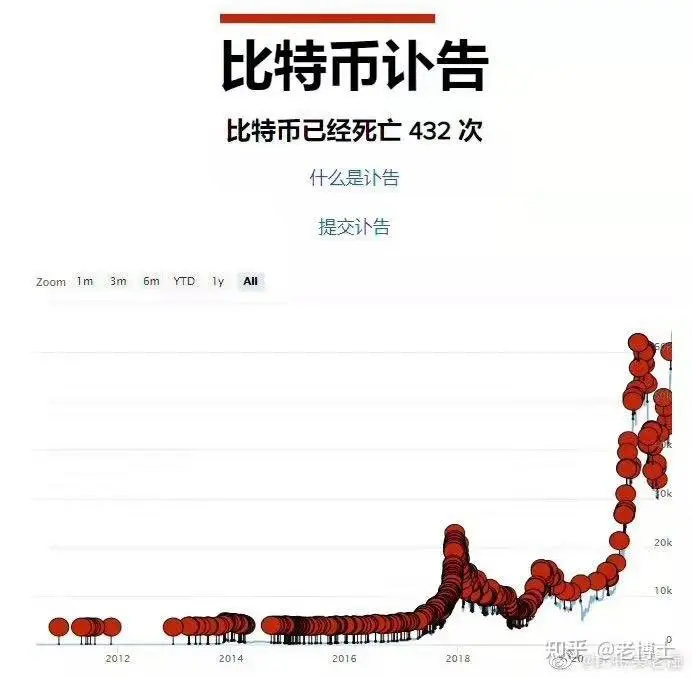
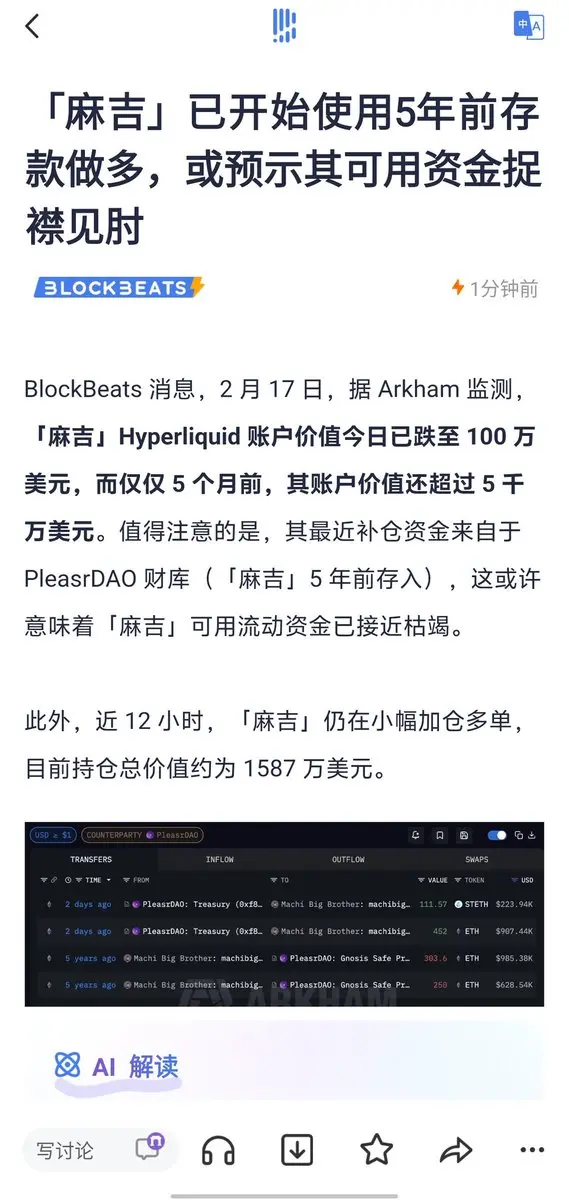
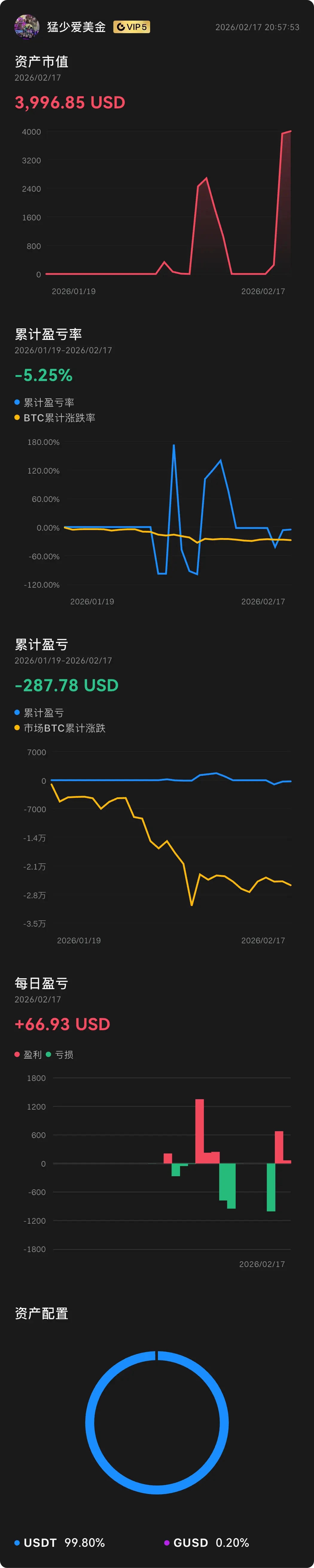
#USCoreCPIHitsFour-YearLow
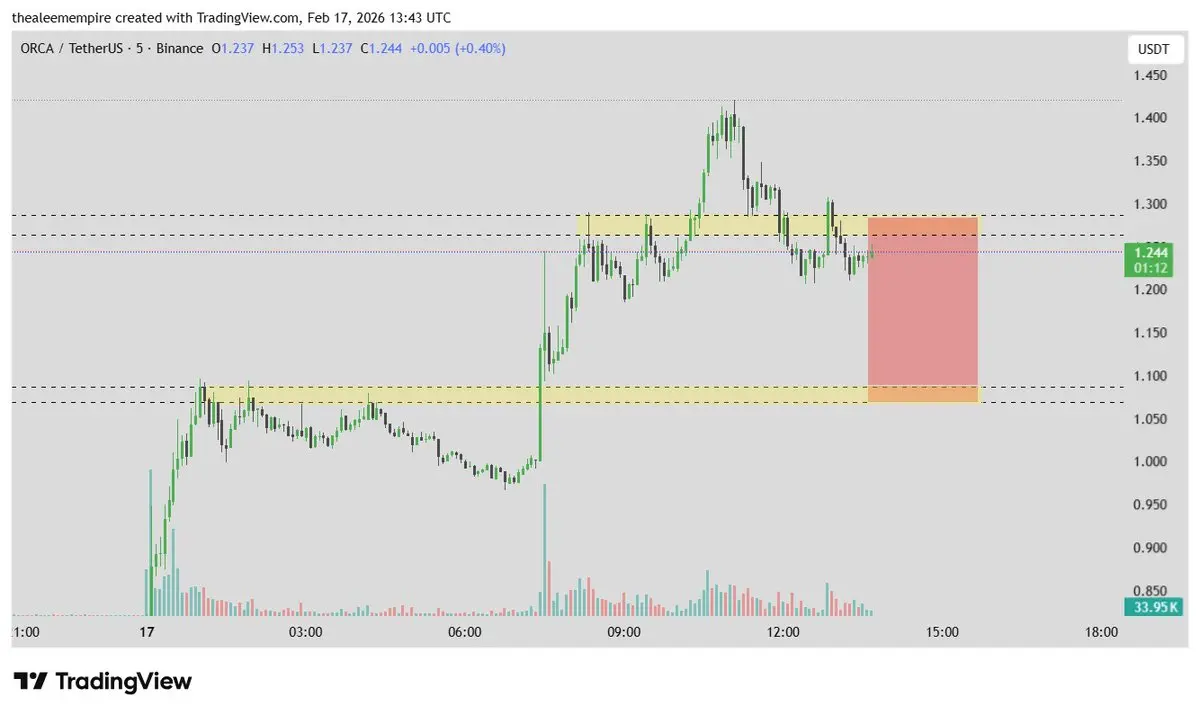
The latest U.S. inflation data for January 2026 has been released, showing a notable slowdown in price pressures. The Consumer Price Index (CPI) report indicates that overall inflation rose modestly over the past year, while the core CPI, which excludes food and energy prices, reached its lowest annual increase in four years. This reflects a meaningful easing of inflationary pressures across the economy and suggests that the U.S. is gradually moving closer to long-term price stability targets.
Core CPI increased by 2.5 percent year-over-year, marking the smallest rise since early 2021. This is below many market expectations and demonstrates a clear moderation compared to late 2025. Month-over-month growth in January was relatively moderate, signaling that inflation is easing steadily. Analysts attribute this improvement to lower energy costs, including gasoline, and more moderate increases in services and other essential categories.
This data is particularly significant for policymakers, as core inflation is a key measure used by the Federal Reserve to gauge underlying price pressures and determine monetary policy. The current readings suggest that inflation may be entering a more stable phase, which could influence future decisions regarding interest rates and policy interventions. Financial markets are likely to respond to these trends, with investors adjusting expectations for interest rate changes, borrowing costs, and investment strategies.
However, experts caution that a single report cannot fully determine future inflation or monetary policy paths. While the four-year low in core CPI is encouraging, the Fed will continue to monitor wage growth, labor market conditions, and consumer spending before making any policy adjustments. Ongoing analysis of these factors is critical to ensuring sustainable price stability without negatively impacting economic growth.
For businesses and consumers, this development is generally positive. Slower price increases can enhance household purchasing power, reduce cost uncertainty, and support financial planning. In broader terms, easing inflation can also help stabilize markets, promote investor confidence, and reinforce expectations for steady economic growth throughout the year.
In summary, the January 2026 CPI report highlights progress in reducing inflationary pressures. While headline inflation remains above some long-term targets, the notable moderation in core prices reflects underlying stability in the economy. Policymakers, economists, and market participants will continue to monitor upcoming data releases closely to assess the trajectory of inflation and its implications for economic policy, financial markets, and broader consumer behavior.
The latest U.S. inflation data for January 2026 has been released, showing a notable slowdown in price pressures. The Consumer Price Index (CPI) report indicates that overall inflation rose modestly over the past year, while the core CPI, which excludes food and energy prices, reached its lowest annual increase in four years. This reflects a meaningful easing of inflationary pressures across the economy and suggests that the U.S. is gradually moving closer to long-term price stability targets.
Core CPI increased by 2.5 percent year-over-year, marking the smallest rise since early 2021. This is below many market expectations and demonstrates a clear moderation compared to late 2025. Month-over-month growth in January was relatively moderate, signaling that inflation is easing steadily. Analysts attribute this improvement to lower energy costs, including gasoline, and more moderate increases in services and other essential categories.
This data is particularly significant for policymakers, as core inflation is a key measure used by the Federal Reserve to gauge underlying price pressures and determine monetary policy. The current readings suggest that inflation may be entering a more stable phase, which could influence future decisions regarding interest rates and policy interventions. Financial markets are likely to respond to these trends, with investors adjusting expectations for interest rate changes, borrowing costs, and investment strategies.
However, experts caution that a single report cannot fully determine future inflation or monetary policy paths. While the four-year low in core CPI is encouraging, the Fed will continue to monitor wage growth, labor market conditions, and consumer spending before making any policy adjustments. Ongoing analysis of these factors is critical to ensuring sustainable price stability without negatively impacting economic growth.
For businesses and consumers, this development is generally positive. Slower price increases can enhance household purchasing power, reduce cost uncertainty, and support financial planning. In broader terms, easing inflation can also help stabilize markets, promote investor confidence, and reinforce expectations for steady economic growth throughout the year.
In summary, the January 2026 CPI report highlights progress in reducing inflationary pressures. While headline inflation remains above some long-term targets, the notable moderation in core prices reflects underlying stability in the economy. Policymakers, economists, and market participants will continue to monitor upcoming data releases closely to assess the trajectory of inflation and its implications for economic policy, financial markets, and broader consumer behavior.