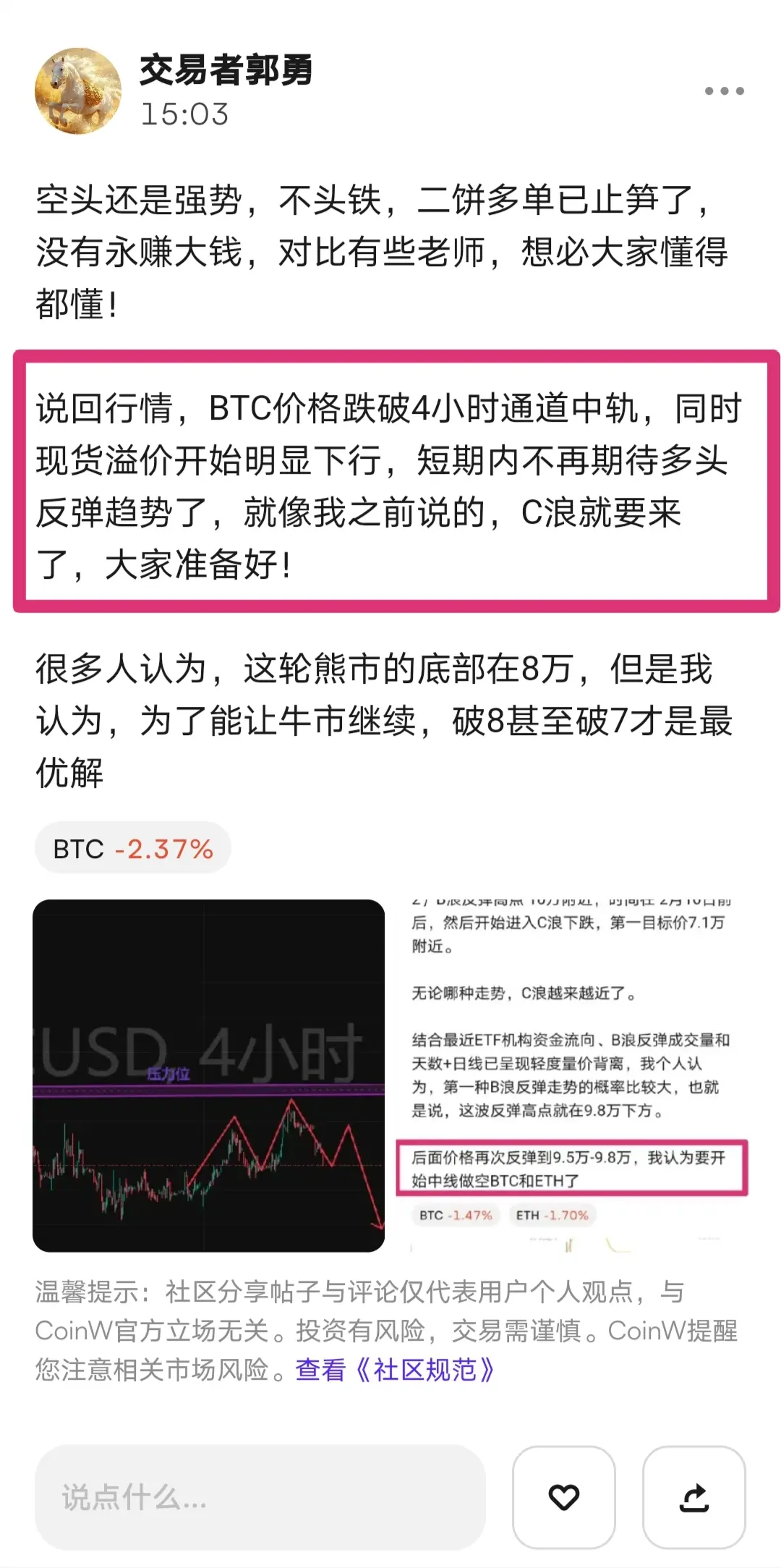
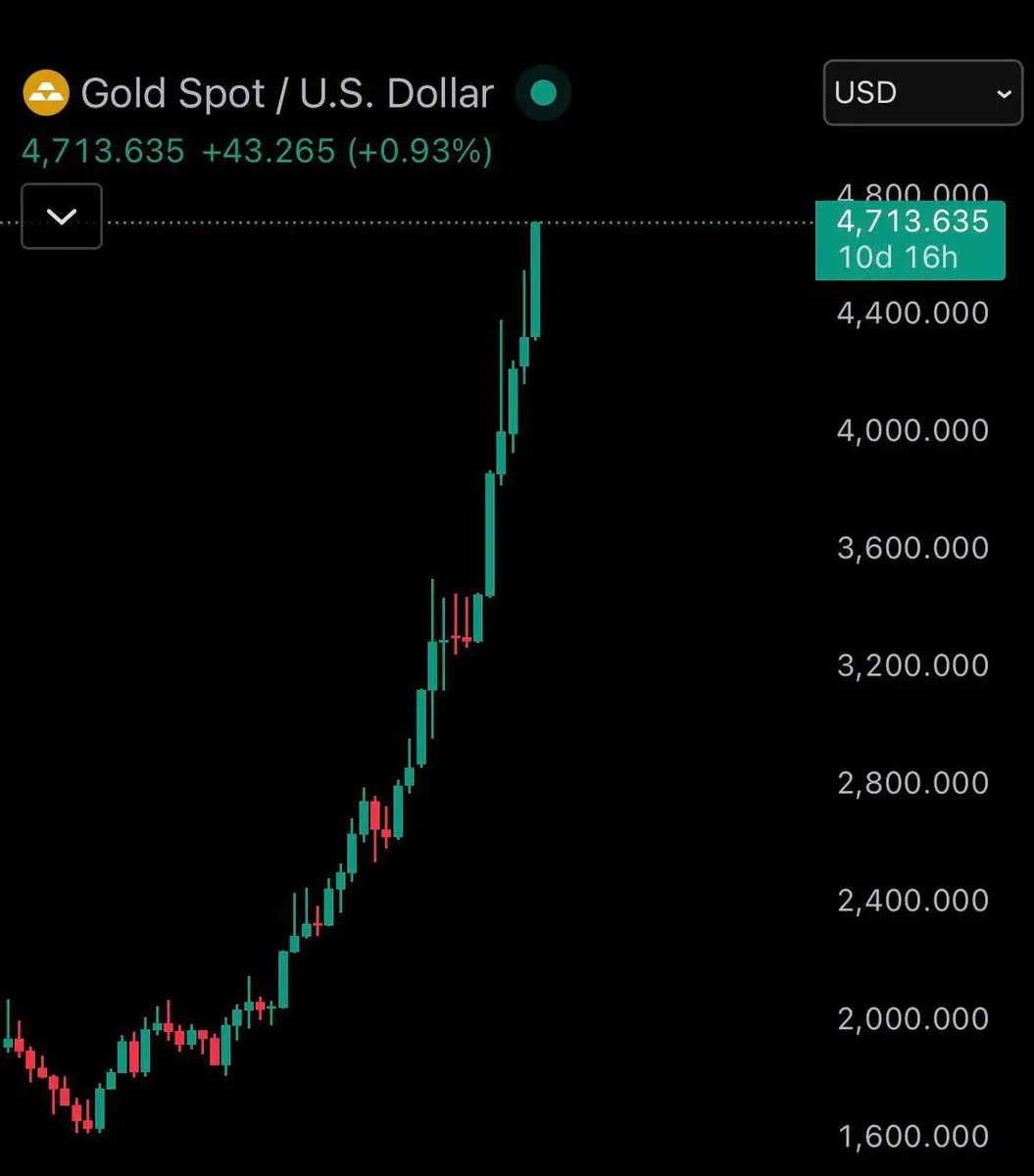
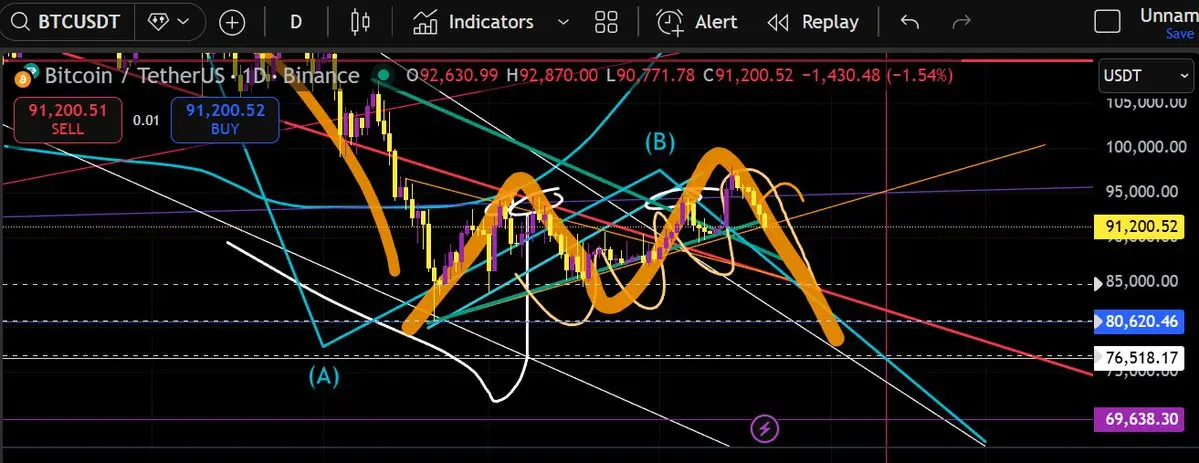
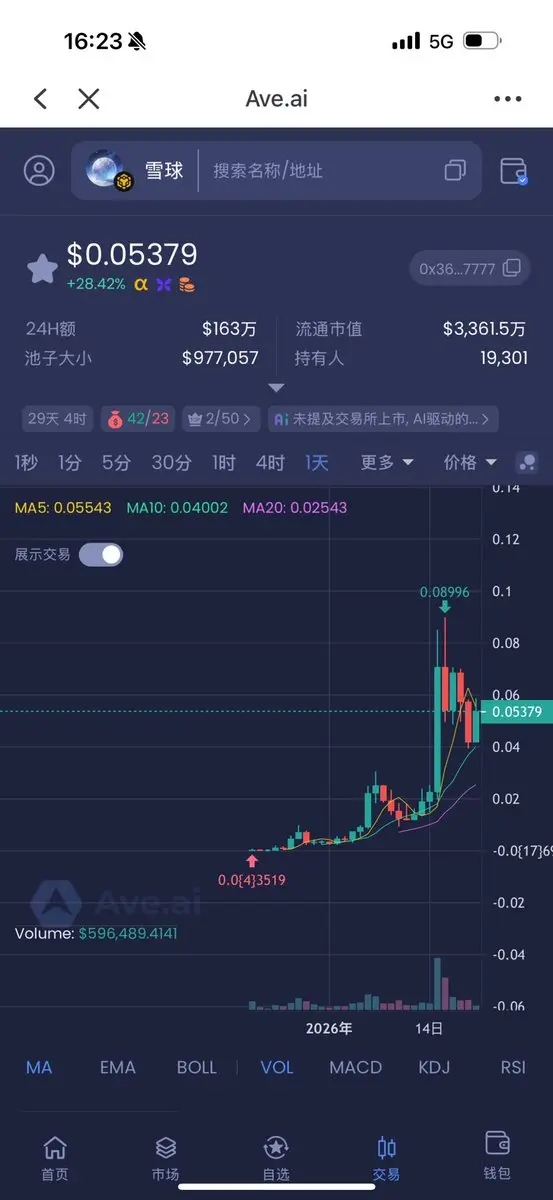
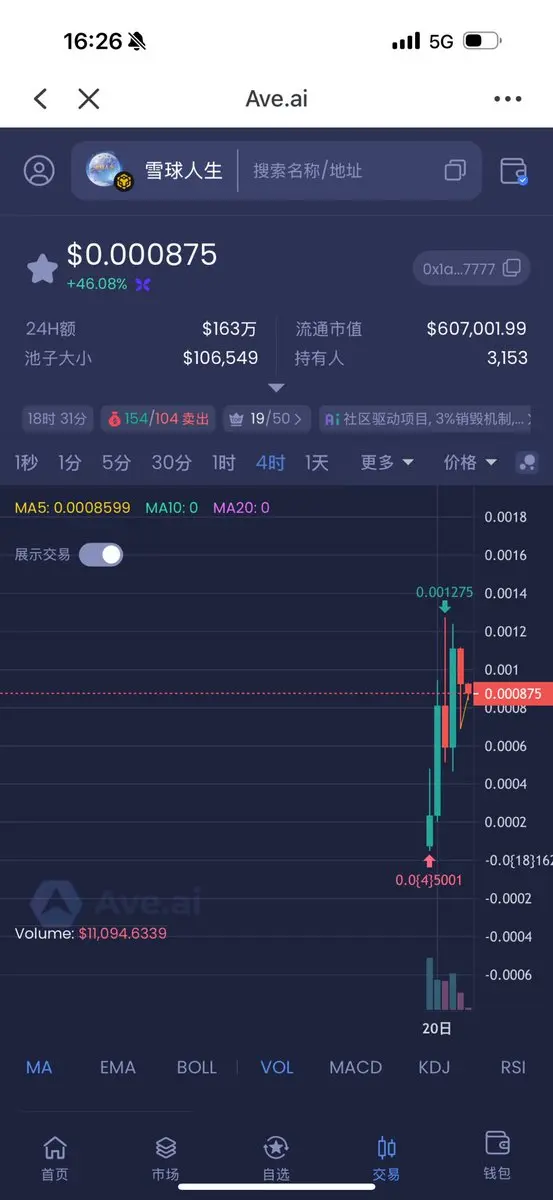
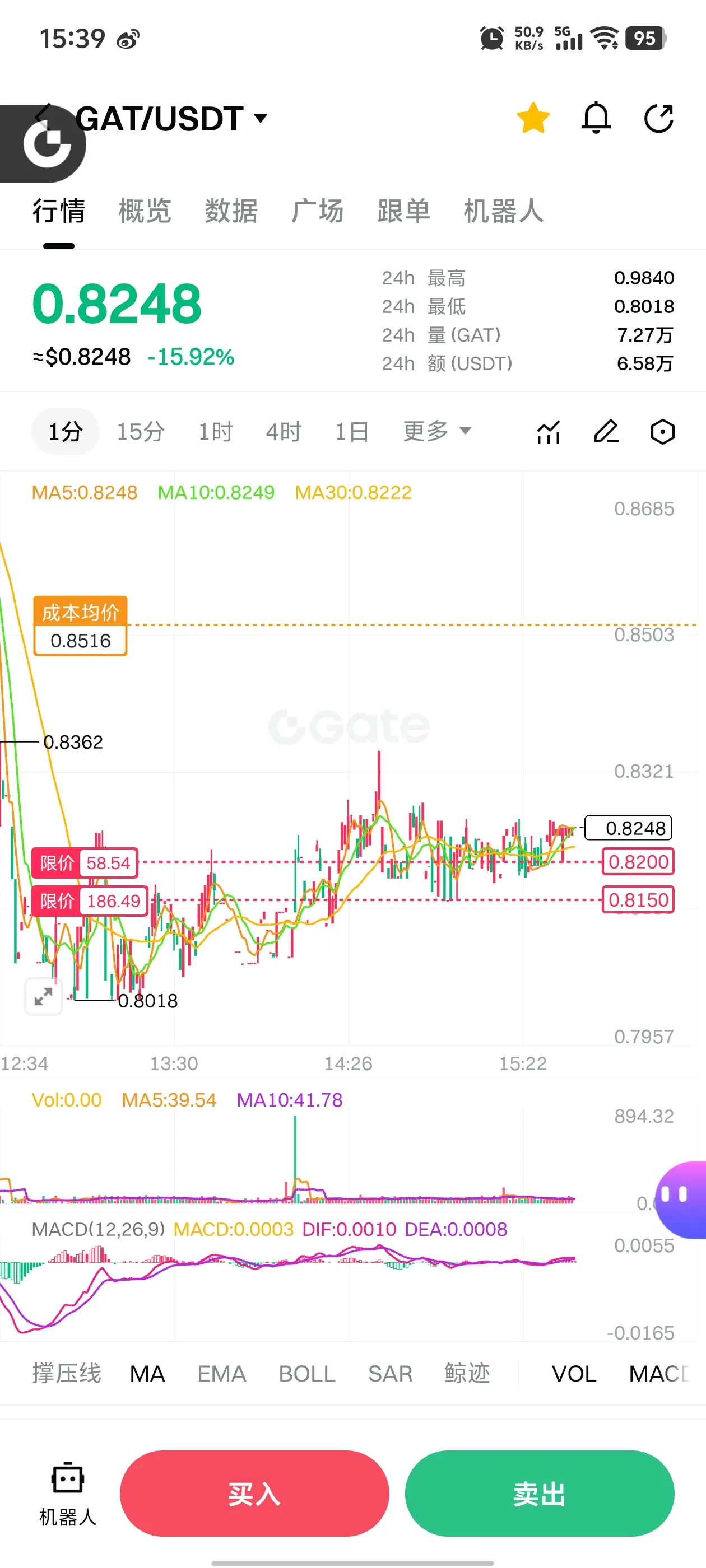
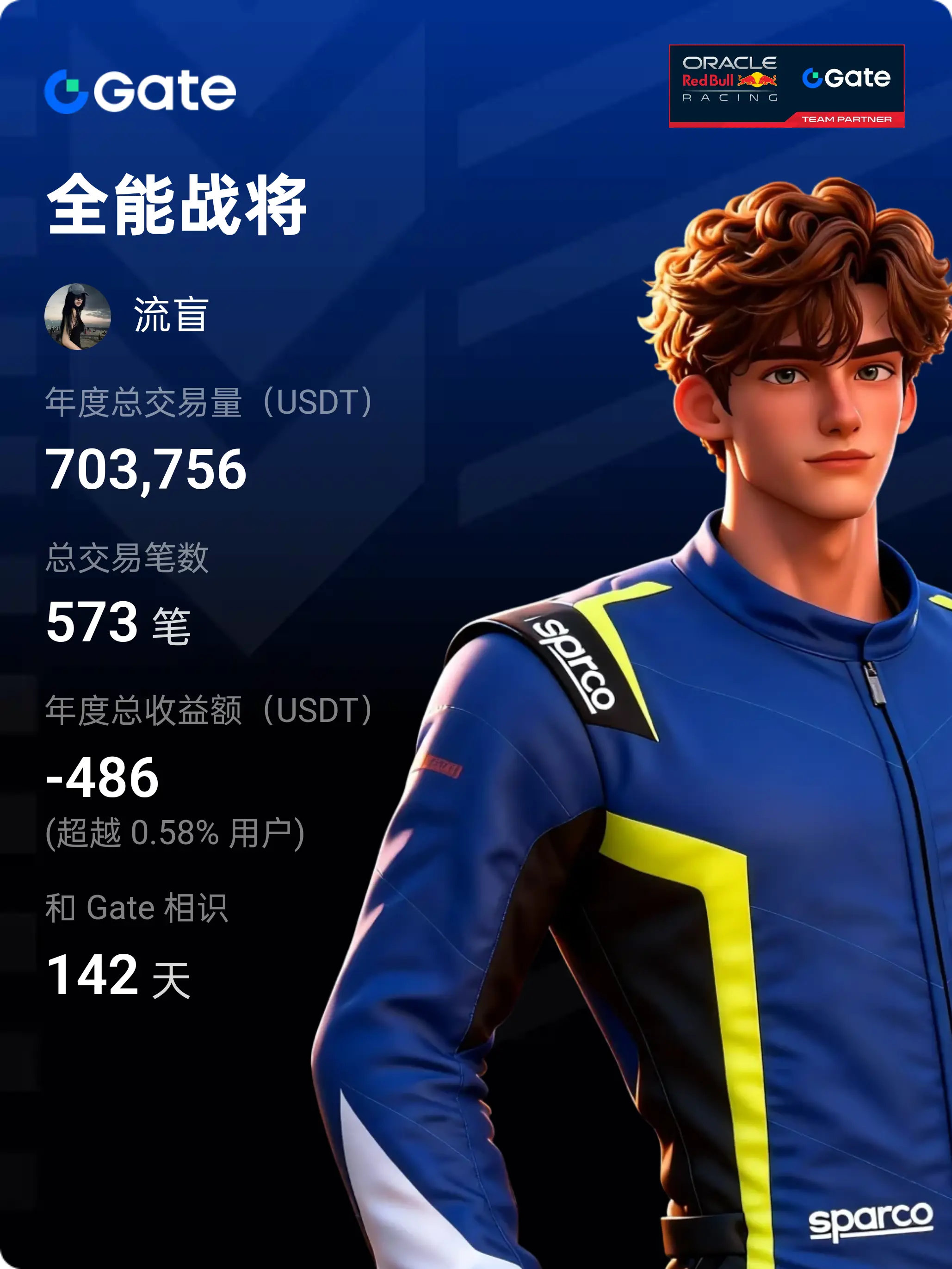
$GAT First, clarify the core conclusion: GAT (Graph Attention Network) is an important branch of GNN, with the core mechanism of dynamically assigning neighbor weights using attention, addressing the limitations of fixed weights in GCN and similar models. It balances adaptability, parallelism, and interpretability, making it suitable for heterogeneous/dynamic graphs and node classification tasks, but it also involves higher computational costs and overfitting risks. The following elaborates on principles, advantages and disadvantages, applications, and practical considerations.
1. Core Prin