Highlights:
①. Gate Intermediate Futures Courses are designed to elevate traders to professional status by developing a robust futures trading system. These courses aim to enhance traders' skills comprehensively, covering investment philosophy, futures trading tools, and trading systems.
②. The piece aims to educate traders on the two margin modes available in futures trading, helping them understand how each mode works, their differences, and when to use each mode for optimal trading.
1. Concepts of Two Margin Modes
①. Cross-Margin Mode
In a cross-margin account, all cross-margin trading pairs share the same margin.If a position incurs significant losses, the entire account's assets may be liquidated to cover those losses.
②. Isolated Margin Mode
Each trading pair corresponds to an independent position, with its own isolated margin. The margin for each position is kept separate, and the profits and losses, as well as the margin rate, are calculated independently for each position. If a position is liquidated, it does not affect the margin or positions of other trading pairs.
2. Differences Between Isolated Margin Mode and Cross-Margin Mode
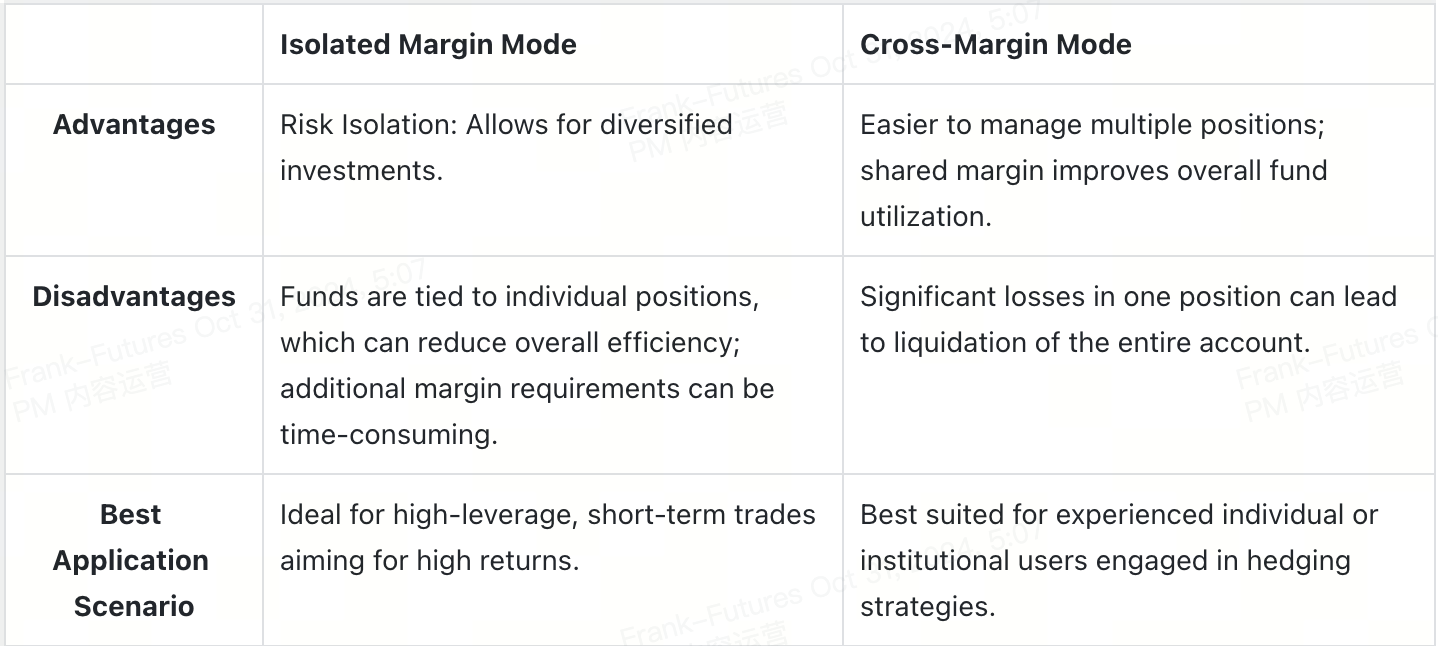
3. Choosing the Best Margin Mode in Futures Trading
In terms of account fund usage, cross-margin mode allows all account funds to be used as margin, shared across multiple positions. This can be understood as putting all your eggs in one basket. Conversely, isolated margin mode calculates margin separately for each position, with profits and losses not affecting other positions. This is like putting your eggs in multiple baskets.
Regarding liquidation risk, in cross-margin mode, positions are interdependent. If the margin is insufficient, the entire account risks liquidation, similar to "grasshoppers on the same string"—if the basket falls, all eggs are broken, and the entire account balance is lost. In isolated margin mode, each position is independent. If one position is liquidated, it does not affect others, akin to having independent baskets—if one falls, the others remain unaffected.
Cross-margin mode is generally suitable for hedging investors, institutions, or experienced users who use it as a hedging tool. Isolated margin mode is better for short-term traders and beginners, as it limits losses to individual positions, making it easier to implement risk control strategies.
4. Summary
In futures trading, cross-margin mode and isolated margin mode are essential operational choices. It is crucial to understand the differences and connections between the two modes to manage position risk effectively and select the most appropriate margin mode.
For practical trading operations, visit the Gate Futures platform. Register for a Gate account now and begin your futures trading journey!

Disclaimer
This article is for informational purposes only and does not constitute investment advice. Gate is not responsible for any investment decisions you make. Content related to technical analysis, market assessments, trading skills, and traders' insights should not be considered a basis for investment. Investing carries potential risks and uncertainties. This article offers no guarantees or assurances of returns on any type of investment.
